Rankine scale
| from Rankine | to Rankine | |
|---|---|---|
| Celsius | [°C] = ([R] − 491.67) × 5⁄9 | [R] = ([°C]+273.15) × 9⁄5 |
| Fahrenheit | [°F] = [R] - 459.67 | [R] = [°F] + 459.67 |
| Kelvin | [K] = [R] × 5⁄9 | [R] = [K] × 9⁄5 |
| For temperature intervals rather than specific temperatures, 1 R = 1 °F = 5⁄9 °C = 5⁄9 K Comparisons among various temperature scales |
||
Rankine is a thermodynamic (absolute) temperature scale named after the Glasgow University engineer and physicist William John Macquorn Rankine, who proposed it in 1859. (The Kelvin scale was first proposed in 1848.)
The symbol for degrees Rankine is R[1] (or Ra if necessary to distinguish it from the Rømer and Réaumur scales). Zero on both the Kelvin and Rankine scales is absolute zero, but the Rankine degree is defined as equal to one degree Fahrenheit, rather than the one degree Celsius used by the Kelvin scale. A temperature of −459.67 °F is exactly equal to 0 R.
Some engineering fields in the U.S. measure thermodynamic temperature using the Rankine scale.[2] However, throughout the entire scientific world thermodynamic temperature is measured in Kelvin.[2] The US National Institute of Standards and Technology does not recommend using degrees Rankine in NIST publications.[1]
Some key temperatures relating the Rankine scale to other temperature scales are shown in the table below.
| Kelvin | Celsius | Fahrenheit | Rankine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute zero (by definition) |
0 K | −273.15 °C | −459.67 °F | 0 R |
| Freezing point of brine (by definition) |
255.37 K | −17.78 °C | 0 °F | 459.67 R |
| Freezing point of water[3] | 273.15 K | 0 °C | 32 °F | 491.67 R |
| Triple point of water (by definition) |
273.16 K | 0.01 °C | 32.018 °F | 491.688 R |
| Boiling point of water[4] | 373.1339 K | 99.9839 °C | 211.97102 °F | 671.64102 R |
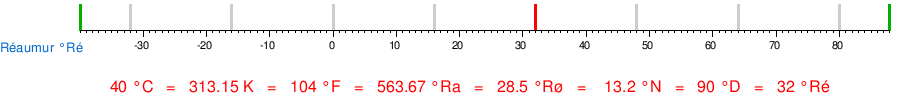
Conversion table between the different temperature units






References
- ^ a b B.8 Factors for Units Listed Alphabetically from Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI), NIST Special Publication 811, 2008 edition, Ambler Thompson and Barry N. Taylor
- ^ a b http://www.physorg.com/tags/temperature/
- ^ The ice point of purified water has been measured to be 0.000089(10) degrees Celsius - see Magnum, B.W. (June 1995). "Reproducibility of the Temperature of the Ice Point in Routine Measurements" (PDF). Nist Technical Note 1411. http://www.cstl.nist.gov/div836/836.05/papers/magnum95icept.pdf. Retrieved 2007-02-11.
- ^ For Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water at one standard atmosphere (101.325 kPa) when calibrated solely per the two-point definition of thermodynamic temperature. Older definitions of the Celsius scale once defined the boiling point of water under one standard atmosphere as being precisely 100 °C. However, the current definition results in a boiling point that is actually 16.1 mK less. For more about the actual boiling point of water, see VSMOW in temperature measurement.
See also
|
|
||||||||